Constipation (Adult)
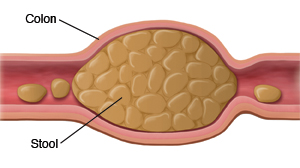
Constipation means that you have less frequent bowel movements (generally fewer than 3 bowel movements a week) than usual. Stools often become very hard and difficult to pass.
Constipation is very common. At some point in life, it affects almost everyone. Since everyone's bowel habits are different, what is constipation to 1 person may not be to another. Your healthcare provider may do tests to diagnose constipation. It depends on what they find when evaluating you.
Symptoms of constipation include:
-
Abdominal pain
-
Bloating
-
Straining during bowel movements
-
Hard, lumpy stools
-
Painful bowel movements
-
Itching, swelling, bleeding, or pain around the anus
-
A feeling that you have not emptied your bowels completely
Causes
Constipation can have many causes. These include:
-
Diet low in fiber
-
Not drinking enough liquids
-
Lack of exercise or physical activity (especially true for older adults)
-
Changes in lifestyle or daily routine, including pregnancy, aging, work, and travel
-
Frequent use or misuse of laxatives
-
Ignoring the urge to have a bowel movement or delaying it until later
-
Medicines, such as certain prescription pain medicines, iron supplements, antacids, certain antidepressants, and calcium supplements
-
Too much dairy
-
Conditions or diseases like irritable bowel syndrome, bowel obstructions, stroke, diabetes, thyroid disease, Parkinson disease, hemorrhoids, and colon cancer
Complications
Possible complications of constipation can include:
-
Hemorrhoids
-
Rectal bleeding from hemorrhoids or anal fissures (skin tears around the anus)
-
Hernias
-
Chronic constipation
-
Fecal impaction, a severe form of constipation in which a large amount of hard stool is in your rectum that you can't pass
-
Bowel obstruction or perforation
-
Rectal prolapse (a portion of rectum slipped out of the anal opening)
Home care
All treatment should be done after talking with your healthcare provider. This is especially true if you have another medical problem, are taking prescription medicines, or are an older adult. Treatment most often involves lifestyle changes. You may also need medicines. Your healthcare provider will tell you which will work best for you. Follow the advice below to help prevent this problem in the future.
Lifestyle changes
These lifestyle changes can help prevent constipation:
-
Diet. Eat a high-fiber diet, with fresh fruit and vegetables, and reduce dairy intake, meats, and processed foods
-
Fluids. It's important to get enough fluids each day. Drink plenty of water when you eat more fiber. If you are on a diet that limits the amount of fluid you can have, talk about this with your healthcare provider.
-
Regular exercise. Check with your healthcare provider first.
Medicines
Take any medicines as directed. Some laxatives are safe to use only now and then. Others can be taken regularly. While laxatives don't cause bowel dependence, they are treating the symptoms. So your constipation may return if you don't make other changes. Talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have questions.
Prescription pain medicines can cause constipation. If you are taking this kind of medicine, ask your healthcare provider if you should also take a stool softener.
Medicines you may take to treat constipation include:
-
Fiber supplements
-
Stool softeners
-
Laxatives
-
Enemas
-
Rectal suppositories
Follow-up care
Follow up with your healthcare provider if symptoms don't get better in the next few days. You may need to have more tests or see a specialist.
Call 911
Call 911 if any of these occur:
-
Trouble breathing
-
Stiff, rigid abdomen that is severely painful to touch
-
Large amounts of blood in the stool
-
Confusion
-
Fainting or loss of consciousness
-
Rapid heart rate
-
Chest pain
When to get medical advice
Call your healthcare provider right away if any of these occur:
-
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as directed by your healthcare provider
-
Failure to resume normal bowel movements
-
Pain in your abdomen or back gets worse
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Swelling in your abdomen
-
Small amount of blood in the stool
-
Black, tarry stool
-
Weight loss without trying
-
Weakness